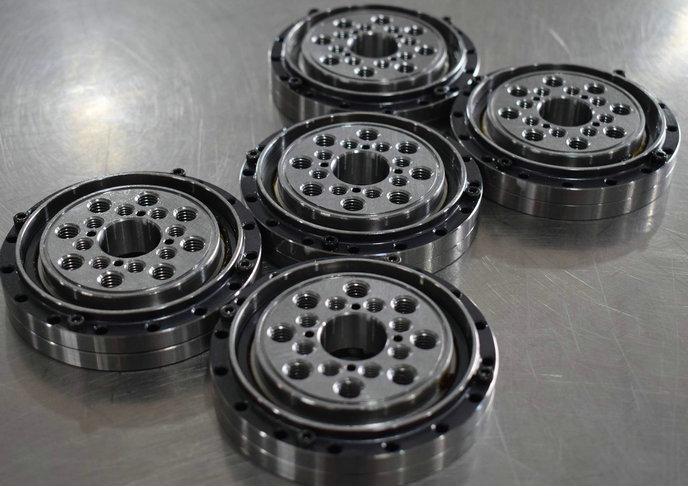
manufacturers of thin-walled equal-section ball rings, precision rollera, drone parts! suppliers of ultra slim equal section ball bearings, industrial robot bearings in china.
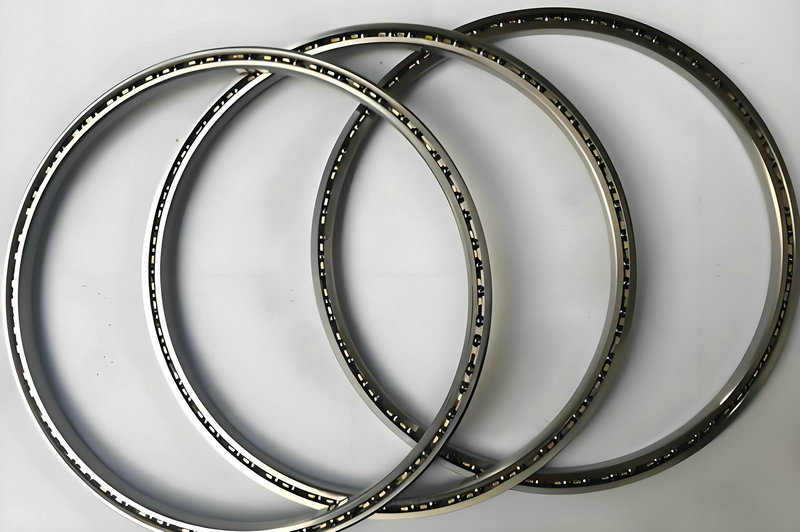

thin wall bearings, as thin-section bearings or slim bearings, are a specialized type of ball bearing or roller bearing designed with an exceptionally thin cross-section relative to their bore diameter. thin wall bearings are engineered to save space while still providing load carrying capabilities, making them suitable for applications with strict size constraints.
thin wall bearings are typically manufactured to high precision standards to ensure accurate performance, especially in applications that require precise positioning and smooth motion. they come in various sizes and configurations, making them versatile for different applications. Some may have seals or shields to protect against contamination.
thin wall bearings are primarily designed to support radial loads. they excel in applications where the primary load is in the radial direction. their primary function is to support radial loads, these bearings can also handle limited axial loads in both directions, but their axial load capacity is generally lower compared to dedicated thrust bearings.
the thin cross-section design contributes to low friction and reduced heat generation during operation, which can improve efficiency and extend bearing life. thin wall bearings are commonly used in the joints and arms of industrial robots, where compactness, precision, and lightweight design are essential. satellite antennas, gimbal systems, aircraft control surfaces, automation systems, conveyor belts, handling equipment.
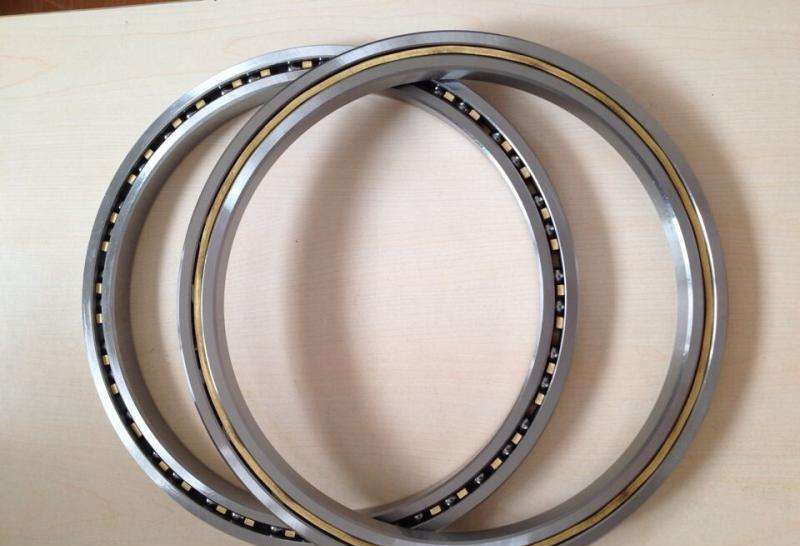
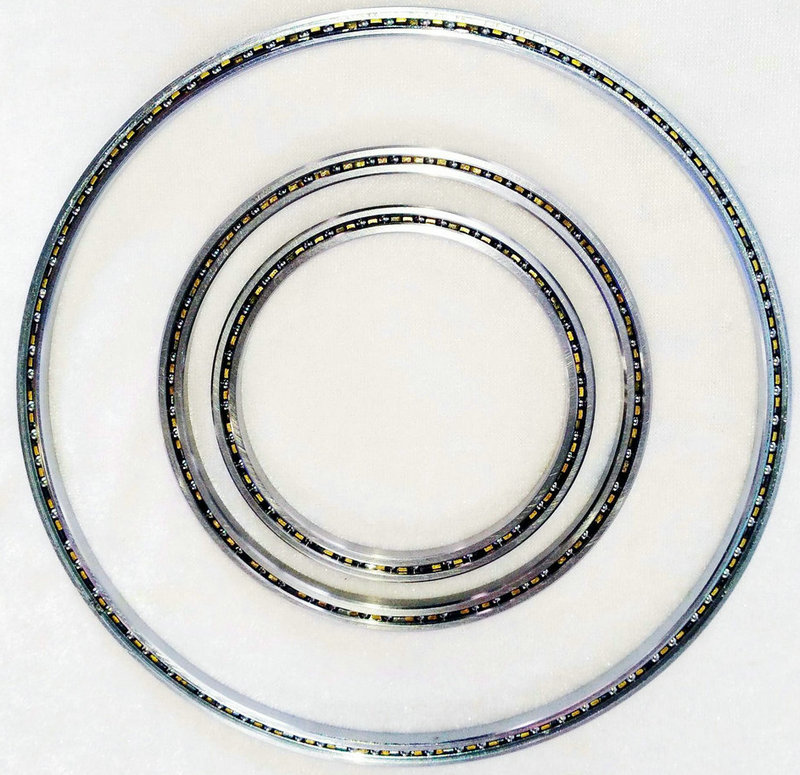


in precision optical instruments like camera gimbals, telescopes, and surveying instruments. surveillance systems, and remote-controlled devices. thin wall bearings are chosen for their ability to provide a balance between load-carrying capacity and space savings. thin cross section allows engineers to design compact and efficient systems without compromising performance. These bearings are available in various sizes and materials to suit different operational requirements.
the most defining feature of thin wall bearings is their extremely thin profile relative to their bore diameter. This characteristic allows them to fit into tight spaces and lightweight structures where conventional bearings may be impractical.

