
YDTech® manufacturer of mill taper dead centers, live chucks, bull nose centers, dead chucks on lathe machines! supplier of lathe long dead centers as dead center points, fixed centers for metal lathes tailstocks in china.
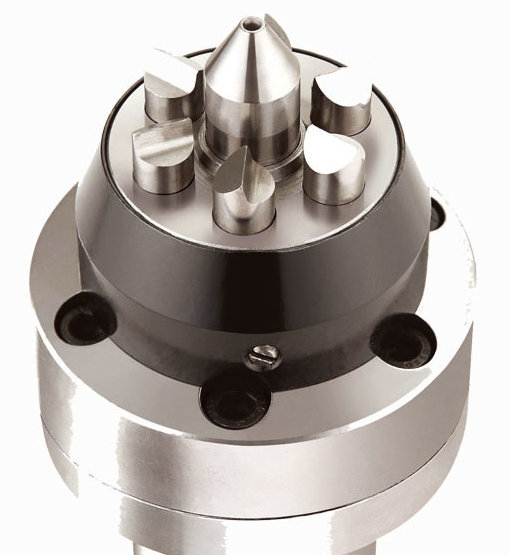

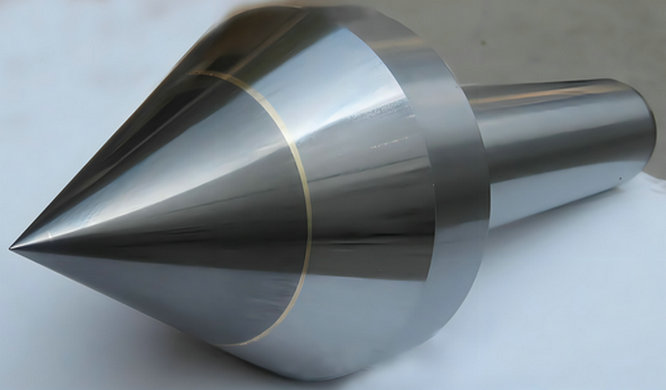
dead centers, as "dead center points" or "fixed centers," are types of lathe centers used in machine tools such as lathes and cylindrical grinders. They are designed to support the non-rotating end of a workpiece during machining operations, providing stability and alignment. Unlike live centers, which rotate along with the workpiece, dead centers remain stationary.
types of dead centers:
soft dead centers,standard dead centers:,hard dead centers, half dead centers
standard dead centers:
Features a pointed center for general-purpose turning operations.
Suitable for a wide range of workpiece materials and applications.
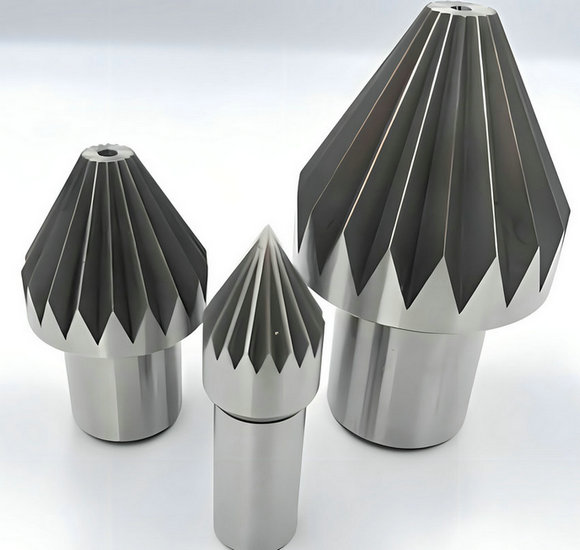
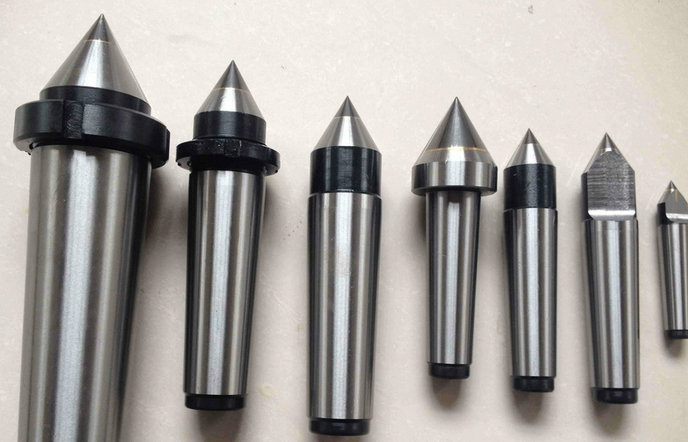


soft dead centers: Has a slightly flattened or rounded point. Designed for workpieces made of softer materials that may deform under pressure.
hard dead centers: Has a sharp, hardened steel point for machining harder materials. Ideal for workpieces that require more precise centering and support.
half dead centers:
Features a half-point design, often used for supporting workpieces with center holes.
Allows for the use of a drill or other tools through the center of the dead center.


Applications of Dead Centers:
Turning Operations: Used in lathes for turning cylindrical workpieces such as shafts, rods, and bushings. Grinding Operations: Support the non-rotating end of the workpiece during cylindrical grinding. Milling and Drilling Operations: Provide stable support for accurate milling and drilling of cylindrical parts. Precision Machining: Used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and toolmaking for high-precision machining tasks.
dead centers are essential tools in machine shops and manufacturing facilities, providing stable support, alignment, and concentricity during turning, grinding, milling, and drilling operations. They offer versatility, durability, and simplicity of design, making them valuable assets for machining a wide range of workpiece materials and sizes. The choice of dead center depends on the specific requirements of the machining task and the characteristics of the workpiece.
Advantages of Dead Centers:
Stability and Support: Dead centers provide stable support for the workpiece, reducing vibration and ensuring accurate machining. Alignment and Concentricity: They help maintain proper alignment and concentricity during turning, grinding, and other machining operations.
Versatility: Dead centers can be used for various workpiece materials and sizes. Durability: Made of hardened steel, dead centers are durable and resistant to wear.
| drive pins (quantity) | drive pins (diameter) | face drivers (diameter) | face drivers bodies | screws | center pins | FD technologies | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 6 | 160 | 60 | 3 | 3.5 | FD 2023 | |||||
| 3 | 8 | 160 | 60 | 3 | 3 | FD 2023Z | |||||
| 3 | 6 | 160 | 42 | 3 | 4.25 | FD 2023F | |||||
| 3 | 8 | 160 | 48 | 3 | 6.25 | FD 2023D | |||||
| 3 | 10 | 160 | 70 | 3 | 6.5 | FD 2023D | |||||
| 3 | 10 | 160 | 70 | 3 | 6.5 | FD 2023HG | |||||
| 3 | 15 | 160 | 80 | 3 | 6 | FD 2023FTY | |||||
| 5 | 15 | 160 | 3 | 90 | 12.5 | FD 2023D | |||||
| 5 | 15 | 160 | 3 | 100 | 12.5 | FD 2023GR | |||||
| 5 | 20 | 160 | 3 | 130 | 12.5 | FD 2023RED | |||||
| 5 | 20 | 220 | 3 | 180 | 12.5 | FD 2023IUI | |||||
| 5 | 20 | 250 | 3 | 220 | 12.5 | FD 2023TT | |||||
| stainless steel drive pins, face driver CNC drive pins, changeable pins, lathe deep face drivers, face driver technologies | |||||||||||
Benefits of fixed centers
Stability: Dead centers provide stable support for the workpiece, minimizing vibration and ensuring accuracy. Alignment: They help maintain proper alignment and concentricity during machining operations. Versatility: Dead centers can be used for a wide range of workpiece materials and sizes. Simple Design: Their straightforward design makes them easy to use and maintain.
- home
- products
- contact
- equipments
- face drivers
- mechanical face drivers
- hydraulic face drivers
- lathe chucks
- tower top face drivers
- live centers
- dead centers
- fixed face drivers
- drill chucks
- CNC tool holders
- custom CNC tools
- drive pins
- drivers vs pins
- S7 drive pins
- lathe drive pins
- mechanical drive pins
- hardened drive pins
- CNC face drivers
- drive fixture pins
- changeable driving pins
- face driver parts
- driving pins